Introductory Skills of Using ADMT Water Detectors for Beginners
1.Basic principles of general geophysical water-finding instruments
Most of the geophysical water-finding instruments on the market use the earth’s natural electric field as the field source to study the electrical structure of the earth’s interior. According to the principle that electromagnetic waves of different frequencies have different skin depths in conductive media, they measure electromagnetic fields of different frequencies on the surface of the earth. After reflecting the electrical changes of geological bodies at different depths, the occurrence characteristics of underground geological bodies can be judged.
Generally, according to the Helmholtz equation of electromagnetic wave propagation theory and the impedance relationship between electromagnetic wave and resistivity, the higher the frequency, the shallower the depth, and the lower the frequency, the deeper the depth. Through the skin depth equation, the resistivity changes at different depths can be expressed, and different geological anomalies can be analyzed and judged. Of course, the attenuation changes of electromagnetic waves (ie attenuation coefficient) need to be considered.
2.Basic use method of general geophysical water-finding instrument
Mainly through two electrodes, namely the MN electrode, the connection between the electrodes is generally 5-20 meters. Or it can be measured by an electromagnetic probe, constantly moving the MN electrode or electromagnetic probe, measuring multiple measuring points and drawing into a cross-sectional color map, a graph, or even a three-dimensional image.
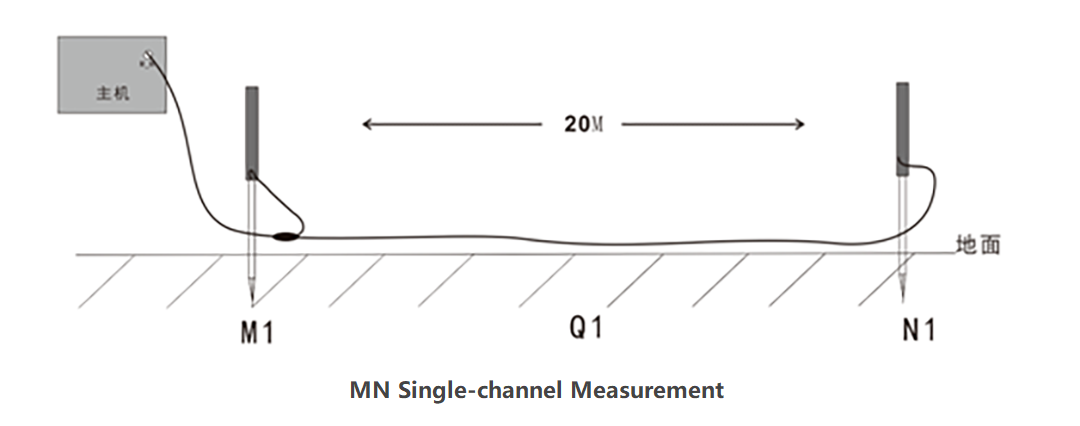
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of MN electrode connection
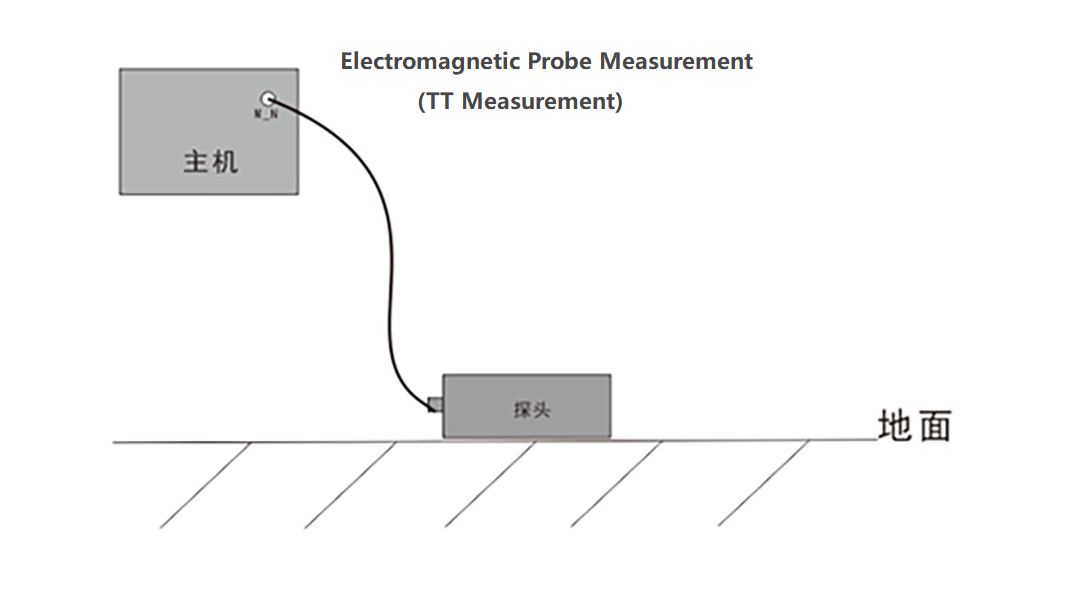
Figure 2: Schematic diagram of electromagnetic probe connection
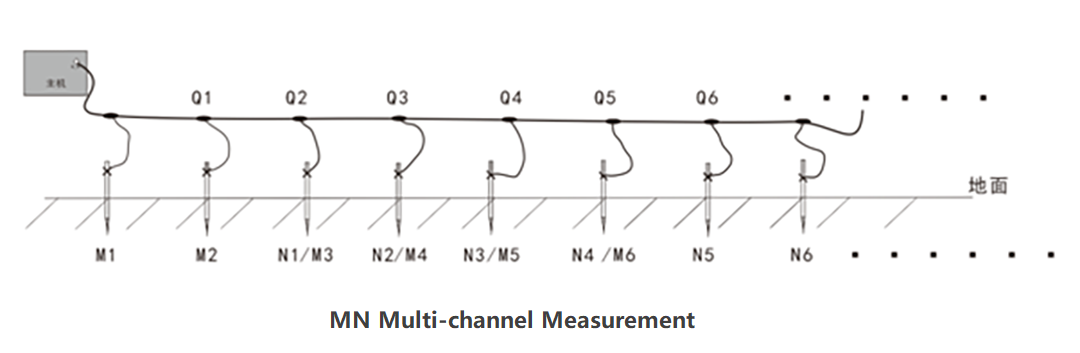
Figure 3: Schematic diagram of multi-channel electrode connection
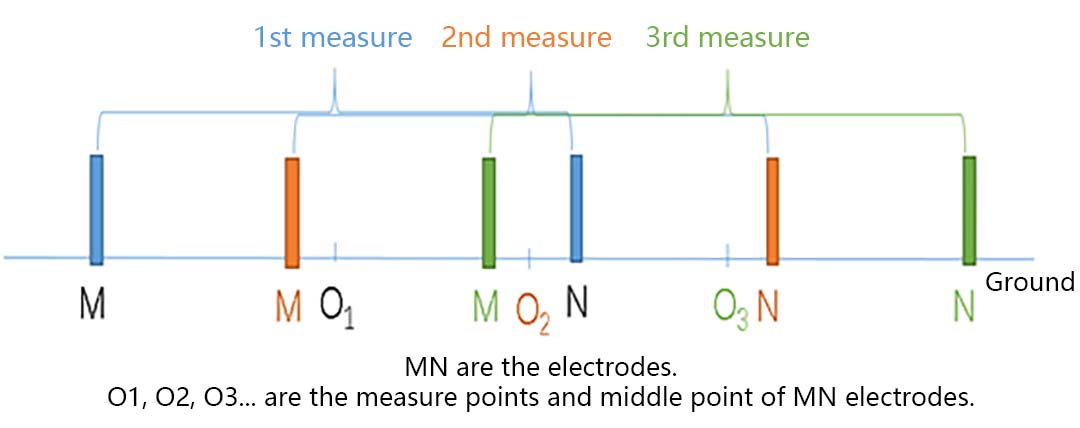
Figure 4: Schematic diagram of MN electrode cross-section movement
Figure 5: Schematic diagram of the cross-section movement of the electromagnetic probe
3.How to arrange the survey line and how to master the survey line direction?
The survey lines of the geophysical water finder are generally straight, and the layout is better. It is best to be perpendicular to the target anomaly that is sought, that is, the direction of groundwater replenishment. Assuming that the recharge direction of groundwater is east-west, the best way to arrange survey lines is north-south. If the recharge direction of groundwater is not known, it can be arranged in a straight line according to the site environment. When laying out, try to consider the ground interference factor and arrange more survey lines. Comprehensive analysis after measurement is better.
4.How many points should be measured for geophysical prospecting water profile measurement points?
Geophysical water-finders generally measure 6 data points to automatically create a map, but in actual measurement, only 6 data points are used to complete the measurement, and if it is judged to drill a well, the success rate may be very low because the amount of measurement data is not enough. , It reflects that the underground information is limited and it is easy to cause misjudgment. Generally, it is recommended that more than 14 points are better. In particular, some small points (such as 1 meter) will cause the survey line to be too short, which makes the entire survey profile above the groundwater or cannot reflect the complete information of the area where the well needs to be drilled, which can easily cause misjudgment.
Therefore, how many points should be measured for the number of measurement points of the geophysical water-finding profile. In fact, the more points the better, and the greater the number of measurement profiles, the better.
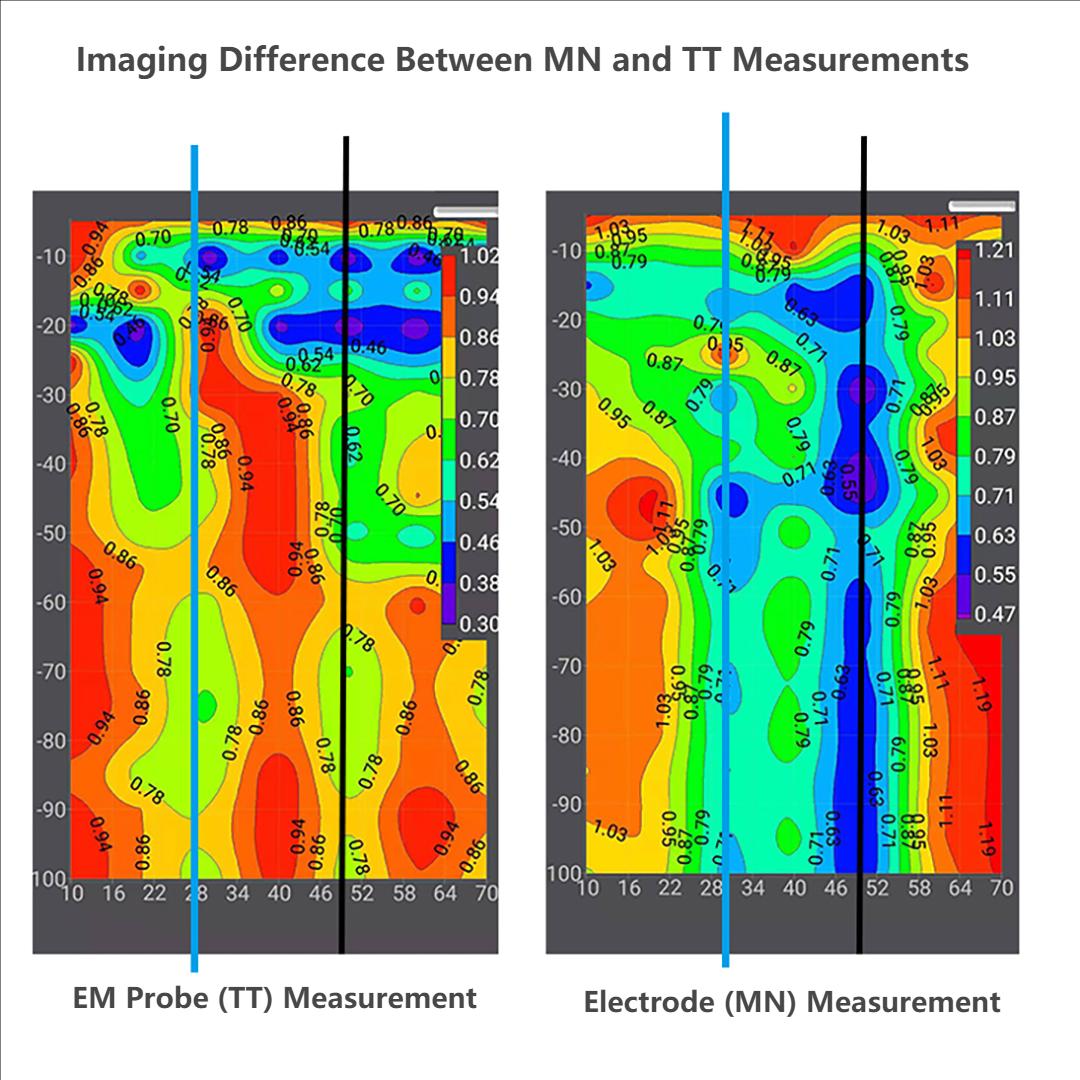
5.What is the difference between electromagnetic probe and MN electrode measurement?
First, the position of the electromagnetic probe measurement point is directly below the probe, and the recording center point of the MN electrode measurement is the center point of the MN electrode;
Secondly, the electromagnetic probe is converted into resistivity by measuring the electromagnetic field, while the MN electrode measurement is directly proportional to the resistivity by measuring the magnitude of the electric field.
Thirdly, the signal measured by the electromagnetic probe in high-resistance areas such as cement ground, rocky ground, desert, etc. is much more stable than the signal measured by the MN electrode, and it can be operated by one person, which is simple and convenient.
It should be noted that there will be some differences in data analysis. It is recommended that the two sensors are used together for better results.
6.Interpretation of several basic terms and basic requirements for geophysical prospecting water profile measurement
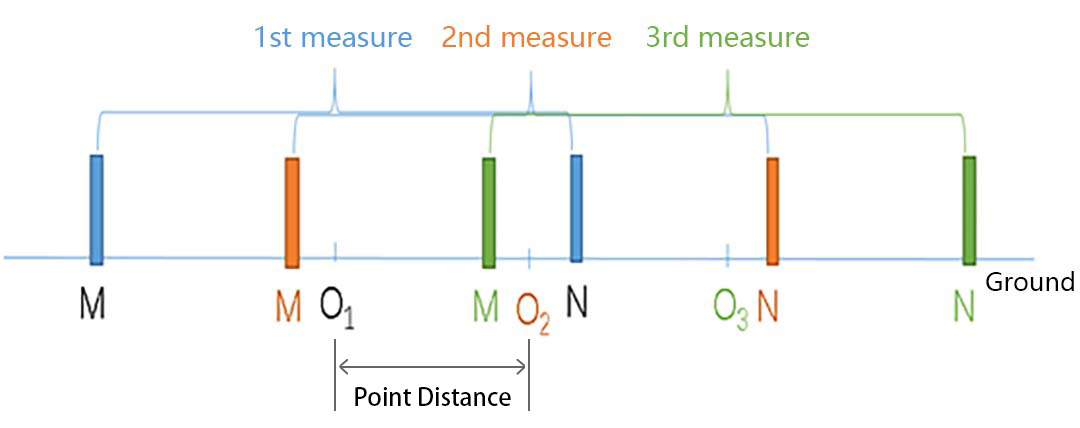
MN spacing: When MN electrodes are measured, the distance between MNs is called MN spacing
Point distance: After measuring one measuring point, the distance to move to the next measuring point is called point distance
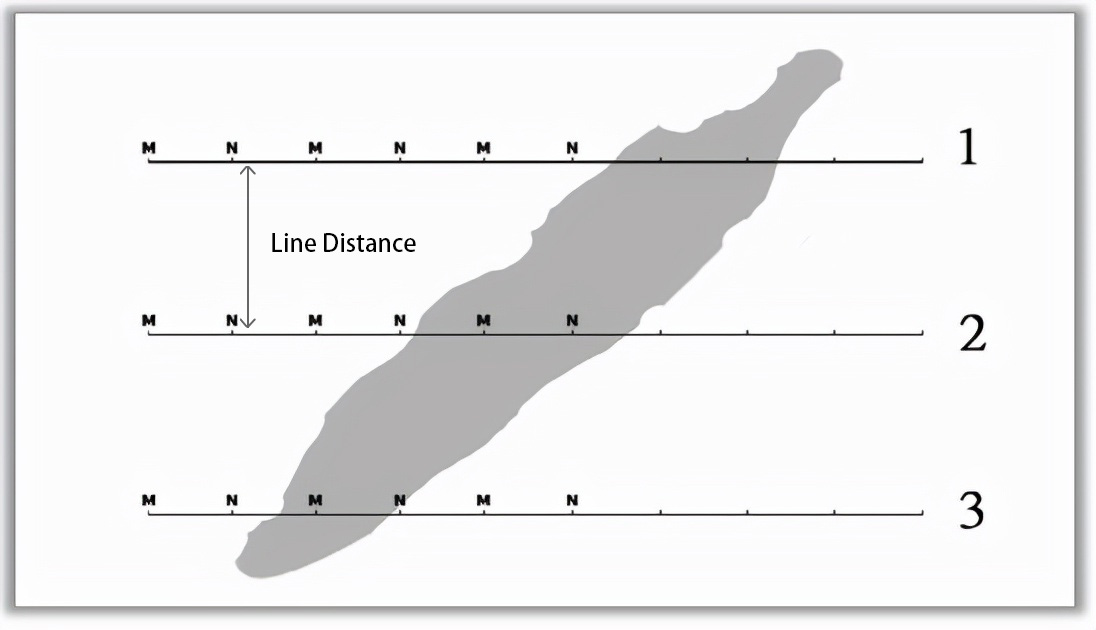
Line distance: After measuring a survey line, or after measuring a profile, measure the direct distance between another survey line and the profile in a parallel direction.
6.1 When measuring with MN electrodes, what is the appropriate MN spacing?
When measuring the MN electrode, the electric field value of the two electrodes (MN electrode) is received to be proportional to the resistivity. Generally, the line length is 5-20 meters. If it is too short, it will easily cause the input signal to be too small, and the interference will be large, which will greatly reduce measurement accuracy.
6.2 What is the appropriate point spacing of the geophysical water-finding profile?
The point distance is generally between 1-5 meters. It is mainly based on the type of groundwater and the target water output. Generally, if the water output is not large, you can choose about 2 meters. For quaternary water or those with a large amount of water, you can choose a point distance of 5 meters or even 10 meters. Generally, the larger point distance is selected for plain areas, and smaller for mountainous areas; the smaller point distance is generally selected for small amounts of domestic water, and the point distance for irrigation and industrial water is larger.
6.3 What is the appropriate distance between geophysical prospecting water profile lines?
Many people make a profile when looking for water in geophysical prospecting, or even a very short profile to finish geophysical prospecting work, so the accuracy is relatively poor. Generally, geophysical prospecting for water requires 3 or more parallel sections, which is better. Accurate judgment, and can also judge other relevant information such as the direction of water replenishment, the amount of water output, and so on.





