How to find underground water in desert area?
The salinity of groundwater in desert areas is generally relatively high. Therefore, freshwater with low salinity is a valuable resource for human life and for industrial and agricultural construction. The main directions for finding fresh water sources in desert areas are as follows:
Phreatic waters near rivers
A few rivers might be found in desert areas. In floodplains and low terraces near the rivers, phreatic water usually has a lower salinity affected by the desalination of the river's surface water.
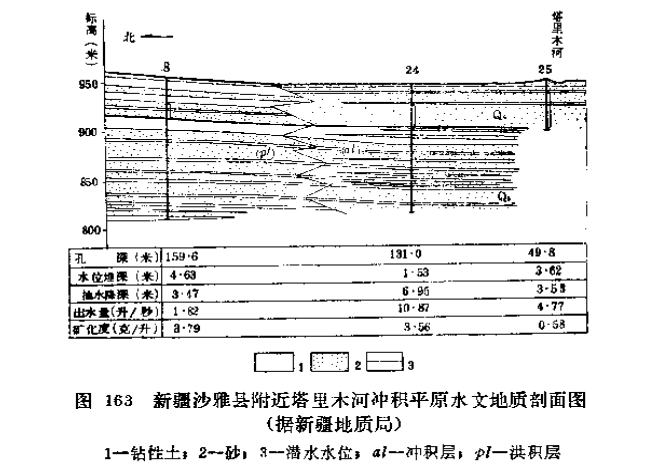
Phreatic waters on the edge of the lake basin
Low-lying areas in desert regions tend to have a few lakes or oases. These lakes or oases are highly seasonal. Fluvial and lacustrine sediments are deposited within the confines of large lake basins and their edges often have groundwater with low salinity.
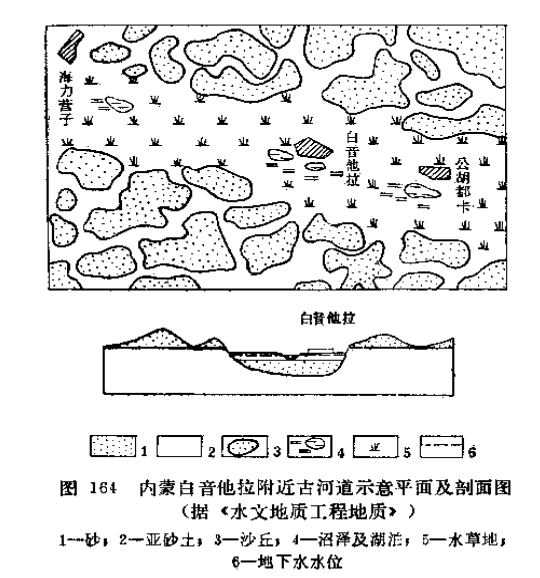
Groundwater in paleochannels
The buried sands formed by the paleochannels are generally rich in groundwater with good quality which can be exploited.
In terms of geomorphology, there are often terrace scarps, trough-shaped depressions as well as small lakes and swamps distributed in bands with water-loving plants. In terms of stratigraphy, paleochannel distribution areas often have a dual structure with overlying clay soil and underlying sand layers. Therefore, people can search for the groundwater by shallow drilling in paleochannels based on geomorphological observations.
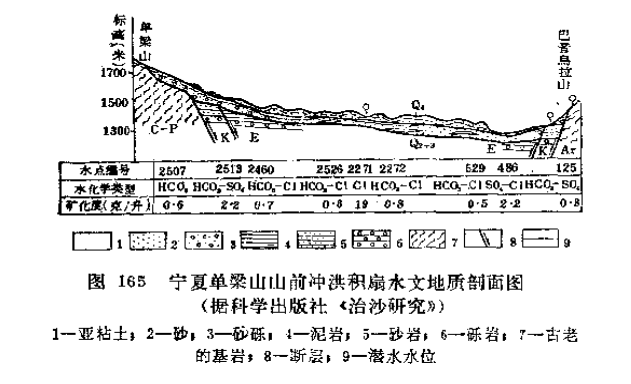
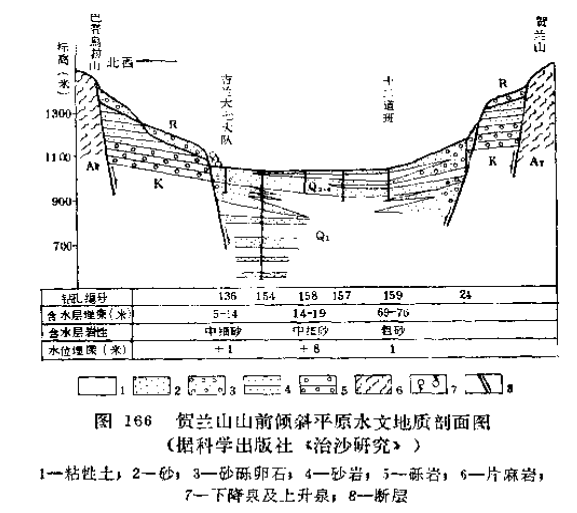
Phreatic waters in alluvial-diluvial fan
There may be some uplifted mountains on the edge of the desert, and alluvial-proluvial fans and sloping plains in front of the mountains often contain freshwater and confined water with relatively low salinity, which are important water supply sources for the desert edge area. The alluvial-proluvial fan aquifer is highly permeable and is recharged by surface runoff making them relatively rich in water.
Confined water in clinoplains
In the deep underground of clinoplains, there are often confined aquifers, in which the confined freshwater can be used as a water supply source.
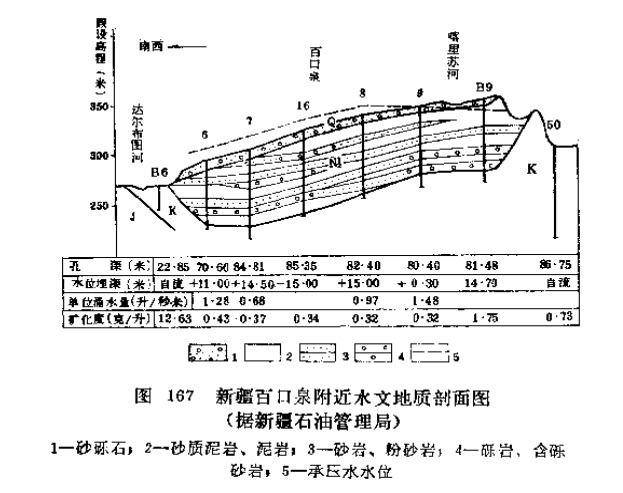
Confined water in Mesozoic and Cenozoic bedrocks
Some of the basins where deserts are widespread are also geologically a tectonic basin in which the Meso-Cenozoic bedrock often contains confined water.
Phreatic waters in the depressions between the dunes
Sand dunes are mainly composed of silt and fine sand with strong permeability. Seasonal precipitation can form freshwater lenses in the wind-eroded dish-shaped depressions and inter-dune depressions. For example, in the Tengger Desert, the aeolian sand is generally 5-50 m thick and the burial depth of phreatic water in the depressions between the hills is generally less than 3 meters. The water inflow from the wells is 8-35 m3/24h and the groundwater salinity is less than 1 g/L.
Groundwater based on surface vegetation
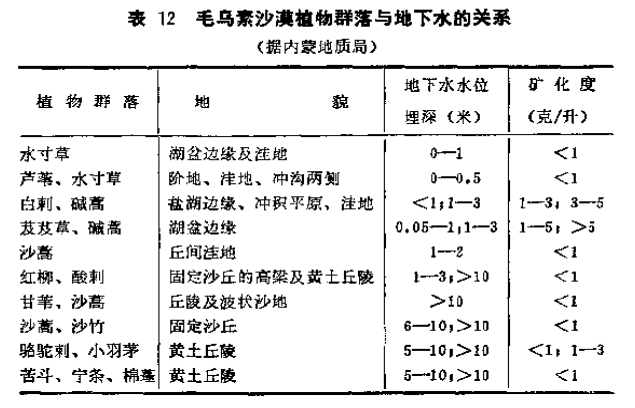
Under different conditions of soil moisture, the types, combinations and generation of plant communities are obviously different. People can judge the depth of groundwater level and the degree of salinity according to these characteristics.